Ohio became the 17th state of the union in 1803 during the presidency of Thomas Jefferson. Prior to statehood, it had been part of the Northwest Territories and governed or overseen by military leaders.

The first was Revolutionary War General Arthur St. Clair, who was a staunch Federalist. St. Clair had intentions of creating two new states that would help the Federalists maintain power in the electoral system. However, he would be replaced, and Charles W. Byrd was put in place the final year before statehood.
After Byrd was put into place and Ohio achieved statehood, the Democratic-Republicans won its first gubernatorial election when Edward Tiffin (the city of Tiffin, Ohio, is named after him) became the first of the Ohio Governors.
The Democratic-Republicans would control the governorship from 1803 - 1826. After 1826, the state would flip back and forth.
Ohio would be considered a swing state for many years, especially during the 20th century. However, the state has voted Republican after the governorship of Ted Strickland, which ended in 2011.
Powers
The governor is the commander-in-chief of the state's National Guard.
The governor has a duty to enforce state laws, the power to either approve or veto bills passed by the Ohio State Legislature, the power to convene the legislature, and the power to grant pardons, except in cases of treason and impeachment.
Other duties and privileges of the office include:
- Executing all laws and requiring written information on any office from the head of that office
- Making an annual address to the General Assembly with recommendations for legislation
- Convening extraordinary sessions of the legislature with limited purposes
- Adjourning the legislature when the two chambers cannot agree to do so themselves, not to include the privilege of adjourning the legislature past the sine die set for the regular session
- Keeping and using "The Great Seal of the State of Ohio"
- Signing and sealing all commissions granted in the name of the state of Ohio
- Nominating, in the event of a vacancy in the Lieutenant Governor's office, a new officer, subject to a confirmatory vote of both chambers of the legislature
- Making vacancy appointments for all "key state officers" (the Auditor, the Treasurer, the Secretary of State, and the Attorney General. Such appointments are for the remainder of the term when the next general election is less than 40 days away and until the next general election otherwise
- Accepting a report from the head of each executive department at least once a year, not later than five days before the regular session of the legislature convenes, and including the substance of those reports in the annual address to the legislature
- Making all appointments not otherwise provided for, with the advice and consent of the Senate, unless the Senate refuses to act, in which case the Governor's appointee takes offices by default
Succession
If one of the Ohio Governors died, resigned, or was convicted of impeachment, the lieutenant governor would then assume the office of governor. This has occurred many times in Ohio history.
If the lieutenant governor's office also became vacant, then the governship would fall to the president of the senate.
If both offices become vacant, then a special election will take place.
Since 1978, the governor and lieutenant governor have been elected on the same ticket; prior to then, they could be members of different parties. This was usually the case prior to the change.
Term Limits
Ohio's first constitution was ratified in 1803 and allowed governors to serve two three-year terms, limited to six of any eight years commencing on the first Monday in December following an election.
The constitution was amended in 1851 to remove the term limit and shift the start of the term to the second Monday in January following an election.
In 1908, Ohio made another change to its gubernatorial elections when it switched from holding elections in odd-numbered years to even-numbered years. This would stagger the elections to be held two years after a presidential election.
In 1957, the constitution was amended to lengthen the term to four years. Governors were allowed to run for re-election once and then were required to wait four years after their second term in a row to run again.
| NAME | PARTY | COUNTY | YEARS | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
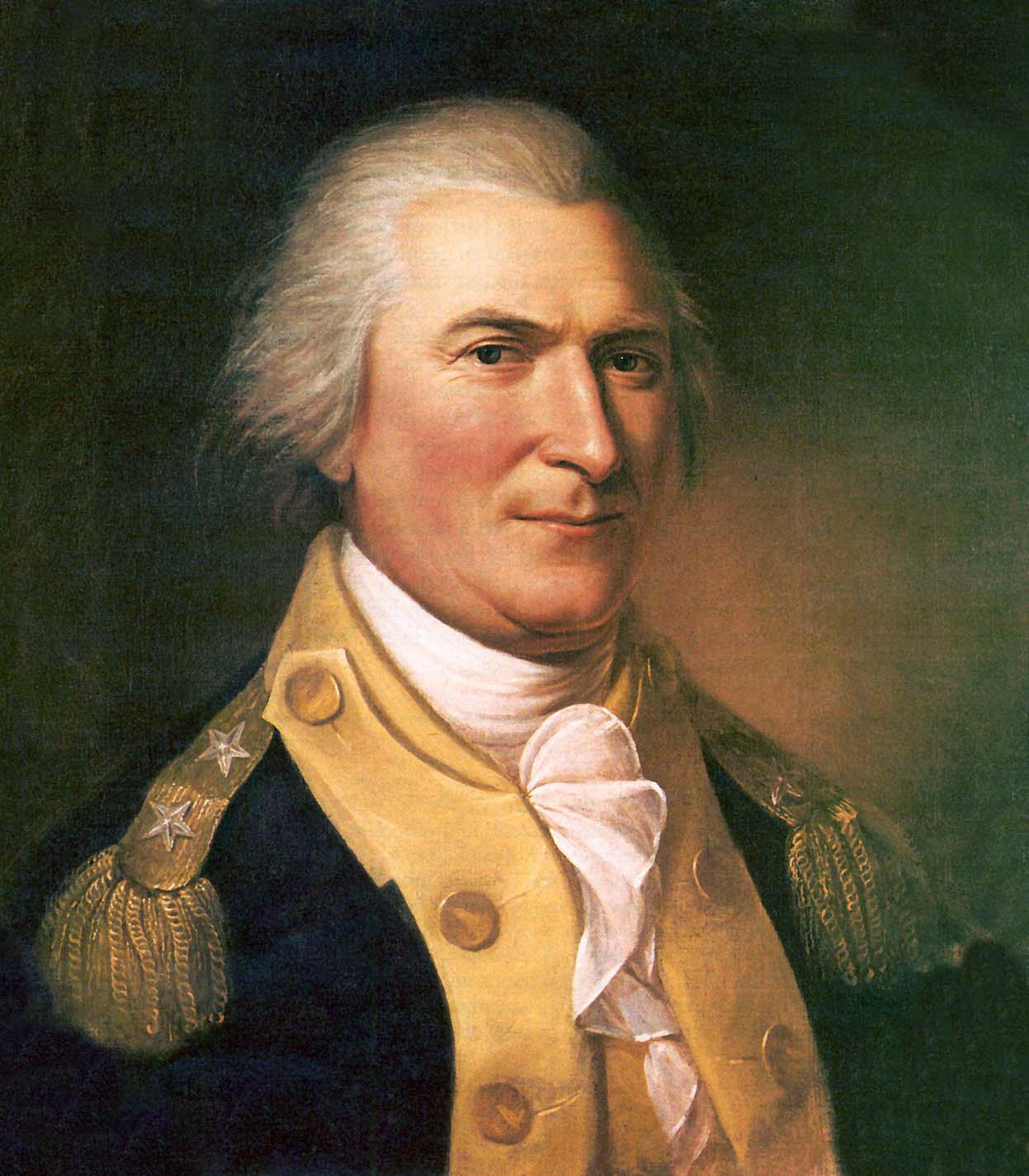

| Arthur St. Clair | Military | 1788 - 1802 | ||

| Charles W. Byrd | Democratic-Republican | 1802 - 1803 | ||
| 1 | 
| Edward Tiffin | Democratic-Republican | Ross | 1803 - 1807 |
| 2 | 
| Thomas Kirker | Democratic-Republican | Adams | 1807 - 1808 |
| 3 |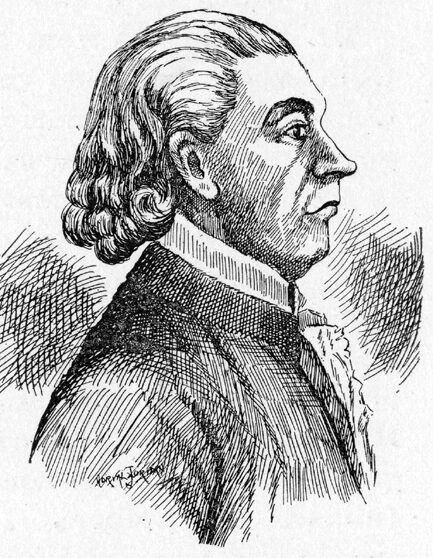 
| Samuel Huntington | Democratic-Republican | Trumbull | 1808 - 1810 |
| 4 | 
| Return J. Meigs Jr. | Democratic-Republican | Washington | 1810 - 1814 |
| 5 | 
| Othniel Looker | Democratic-Republican | Hamilton | 1814 |
| 6 | 
| Thomas Worthington | Democratic-Republican | Ross | 1814 - 1818 |
| 7 | 
| Ethan Allen Brown | Democratic-Republican | Hamilton | 1818 - 1822 |
| 8 |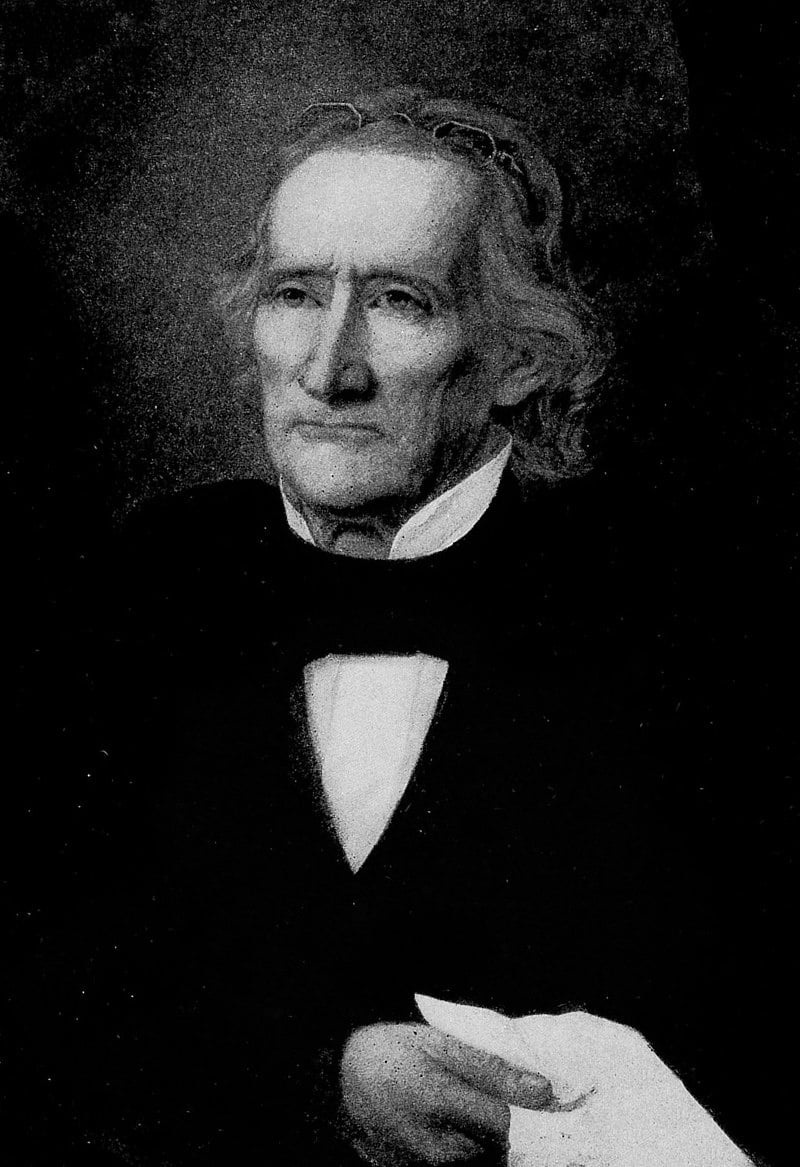 
| Allen Trimble | Federalist | Highland | 1822 |
| 9 | 
| Jeremiah Morrow | Democratic-Republican | Warren | 1822 - 1826 |
| 10 | 
| Allen Trimble | Federalist | Highland | 1826 - 1830 |
| 11 | 
| Duncan McArthur | Federalist | Ross | 1830 -1832 |
| 12 |  | Robert Lucas | Democratic-Republican | Pike | 1832 - 1836 |
| 13 |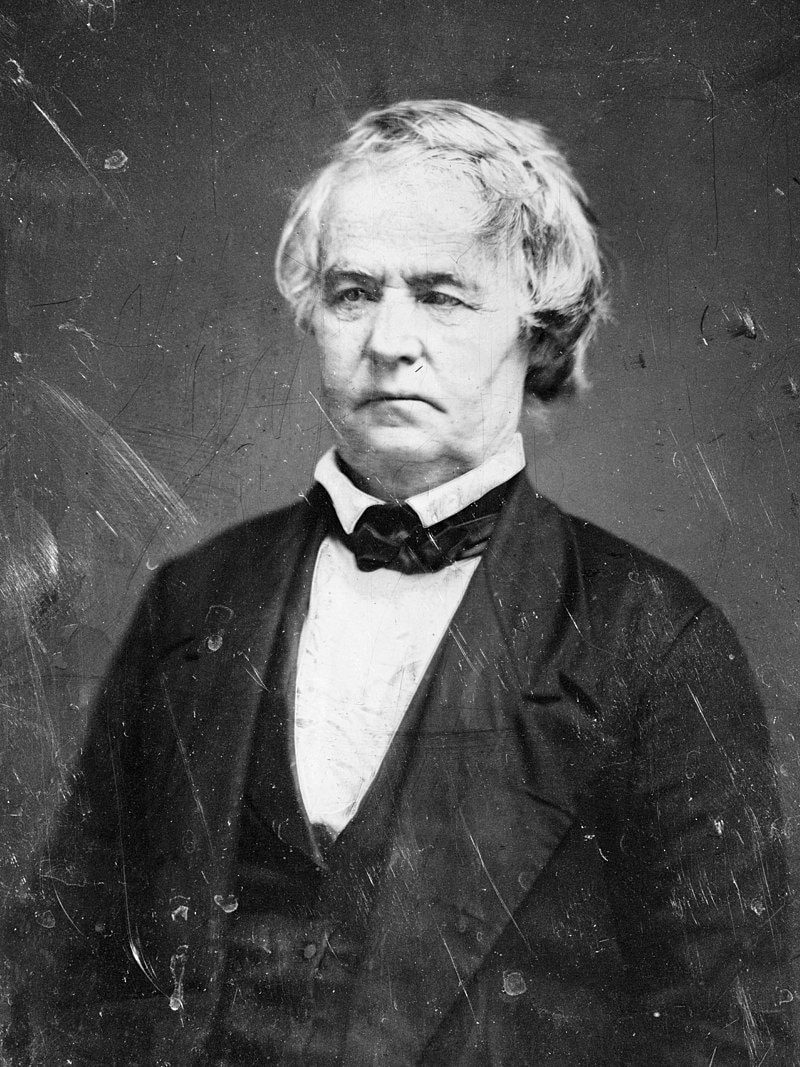 
| Joseph Vance | Whig | Champaign | 1836 - 1838 |
| 14 | 
| Wilson Shannon | Democrat | Belmont | 1838 - 1840 |
| 15 |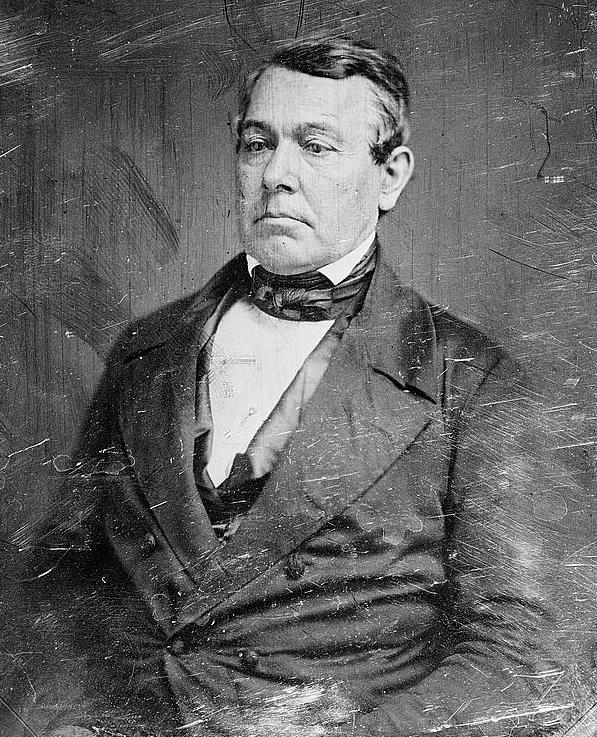 
| Thomas Corwin | Whig | Warren | 1840 - 1842 |
| 16 | 
| Wilson Shannon | Democrat | Belmont | 1842 - 1844 |
| 17 |  | Thomas W. Bartley | Democrat | Richland | 1844 |
| 18 |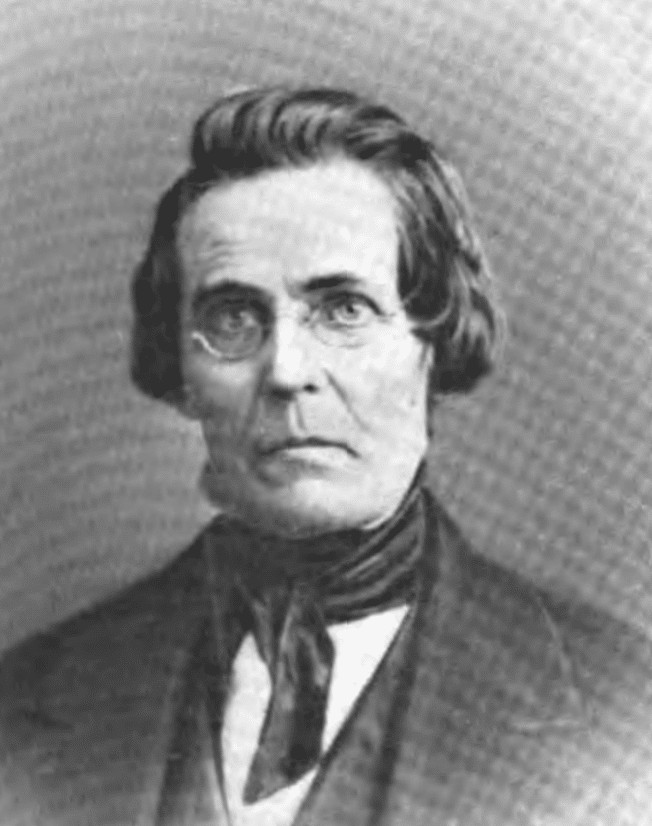  | Mordecai Bartley | Whig | Richland | 1844 - 1846 |
| 19 |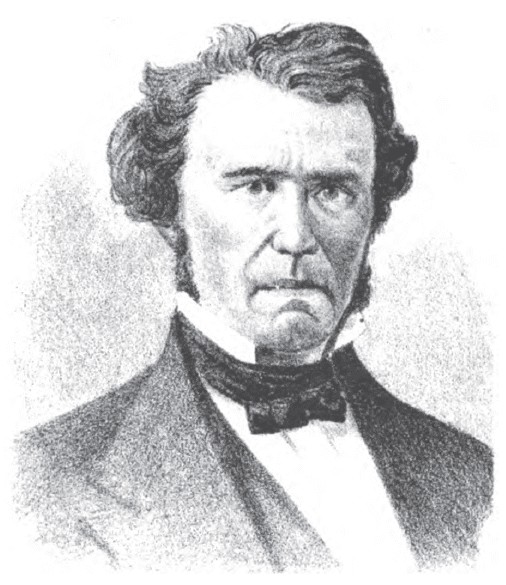  | William Bebb | Whig | Butler | 1846 - 1848 |
| 20 |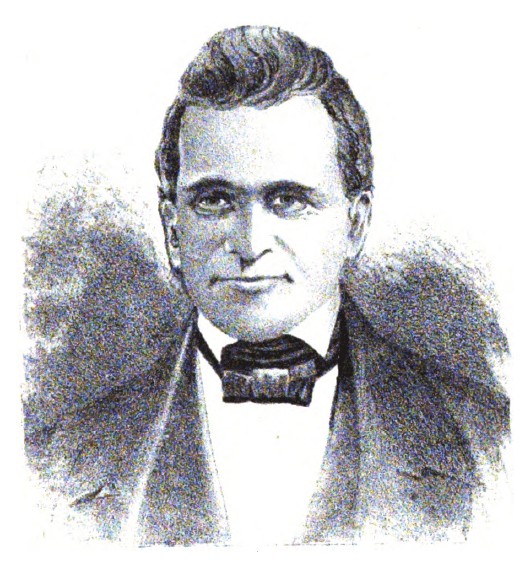  | Seabury Ford | Whig | Geauga | 1848 - 1850 |
| 21 |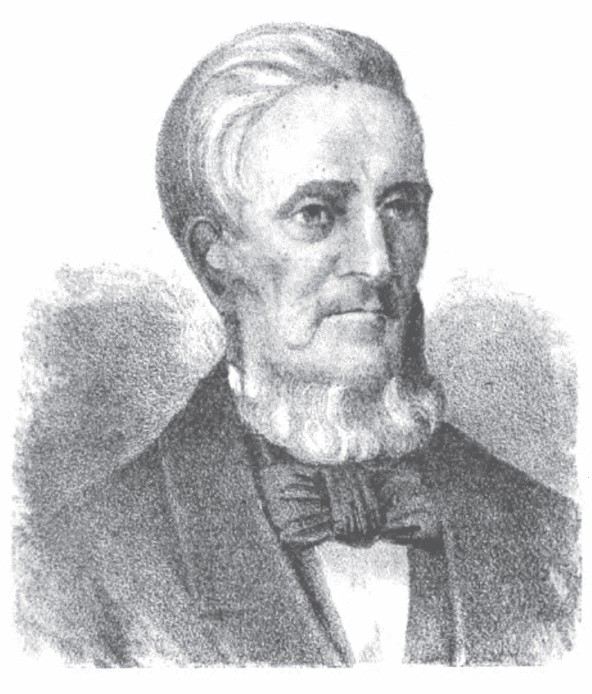  | Reuben Wood | Democrat | Cuyahoga | 1850 - 1853 |
| 22 | 
| William Medill | Democrat | Fairfield | 1853 - 1856 |
| 23 |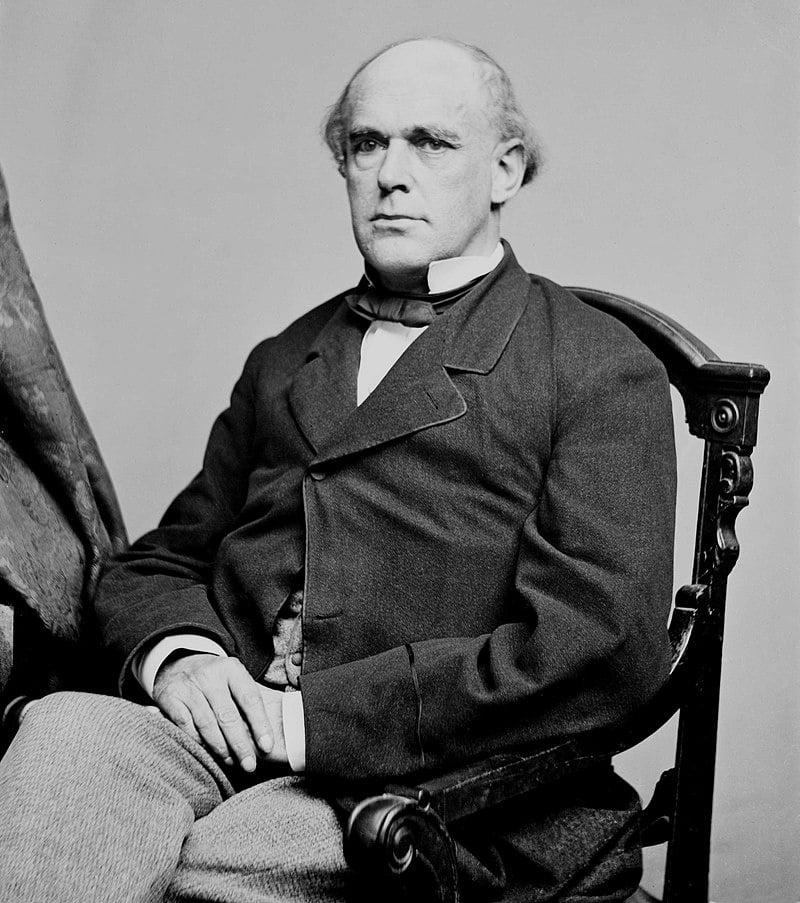 
| Samuel P. Chase | Republican | Hamilton | 1856 - 1860 |
| 24 |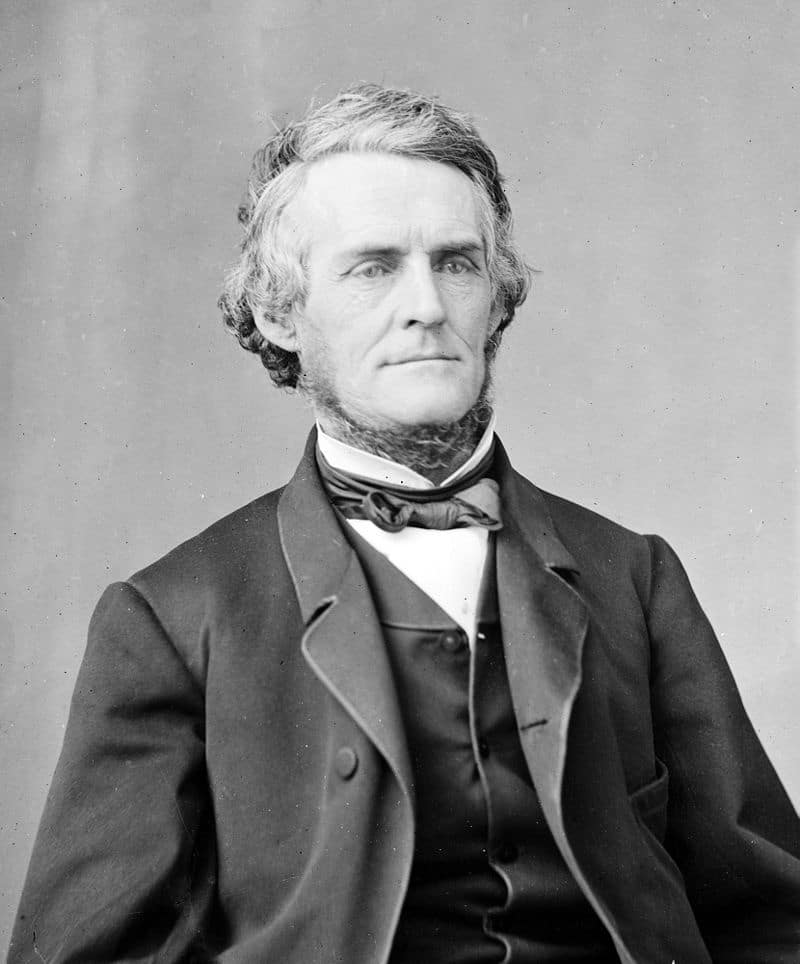 
| William Dennison Jr. | Republican | Franklin | 1860 - 1862 |
| 25 |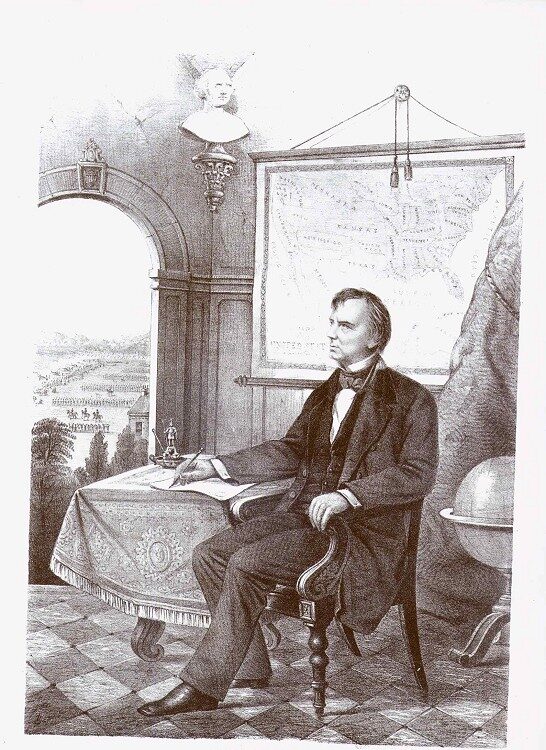 
| David Tod | Republican | Mahoning | 1862- 1864 |
| 26 | 
| Jon Brough | Republican | Cuyahoga | 1864 - 1865 |
| 27 | 
| Charles Anderson | Republican | Montgomery | 1865 - 1866 |
| 28 | 
| Jacob Dolson Cox | Republican | Hamilton | 1866 - 1868 |
| 29 | 
| Rutherford B. Hayes | Republican | Hamilton | 1868 - 1872 |
| 30 | 
| Edward F. Noyes | Republican | Hamilton | 1872 - 1874 |
| 31 | 
| William Allen | Democrat | Ross | 1874 - 1876 |
| 32 | 
| Rutherford B. Hayes | Republican | Sandusky | 1876 - 1877 |
| 33 | 
| Thomas L. Young | Republican | Hamilton | 1877 - 1878 |
| 34 | 
| Richard M. Bishop | Democrat | Hamilton | 1878 - 1880 |
| 35 | 
| Charles Foster | Republican | Seneca | 1880 - 1884 |
| 36 | 
| George Hoadly | Democrat | Hamilton | 1884 - 1886 |
| 37 |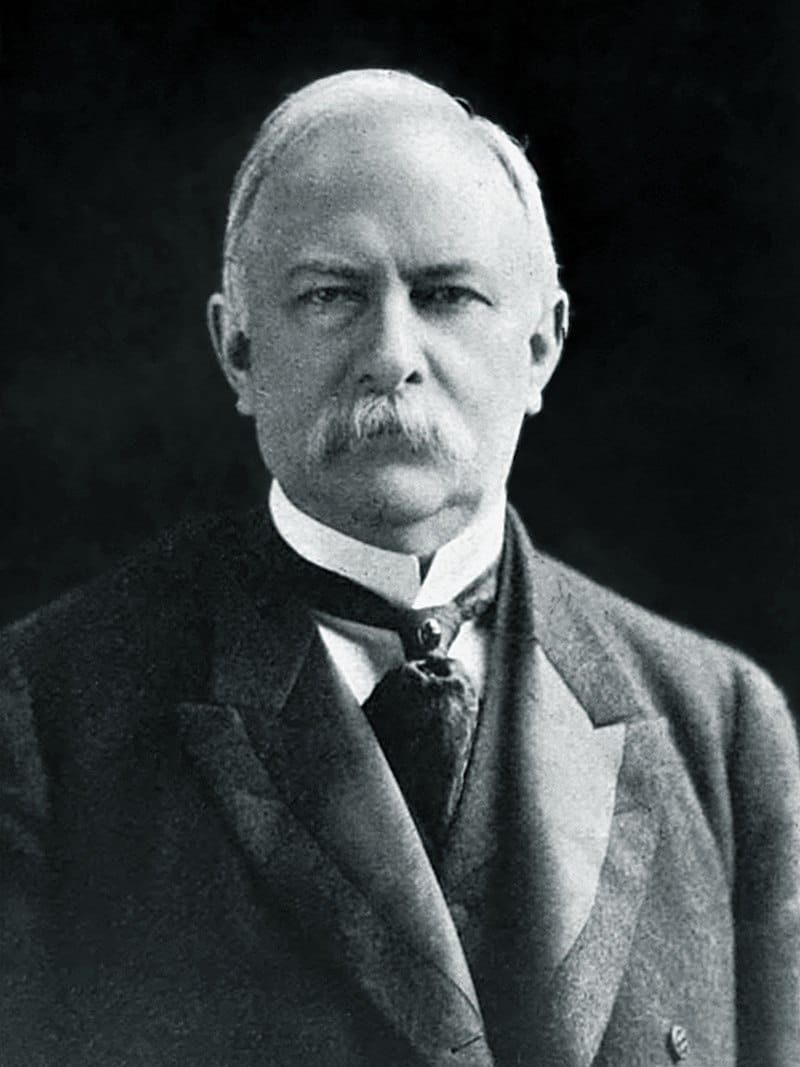 
| Joseph B. Foraker | Republican | Hamilton | 1886 - 1890 |
| 38 |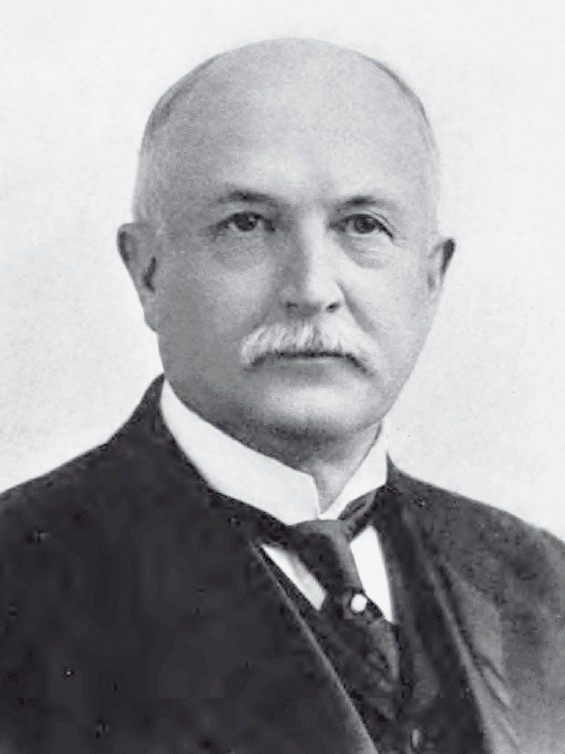  | James E. Campbell | Democrat | Butler | 1890 - 1892 |
| 39 |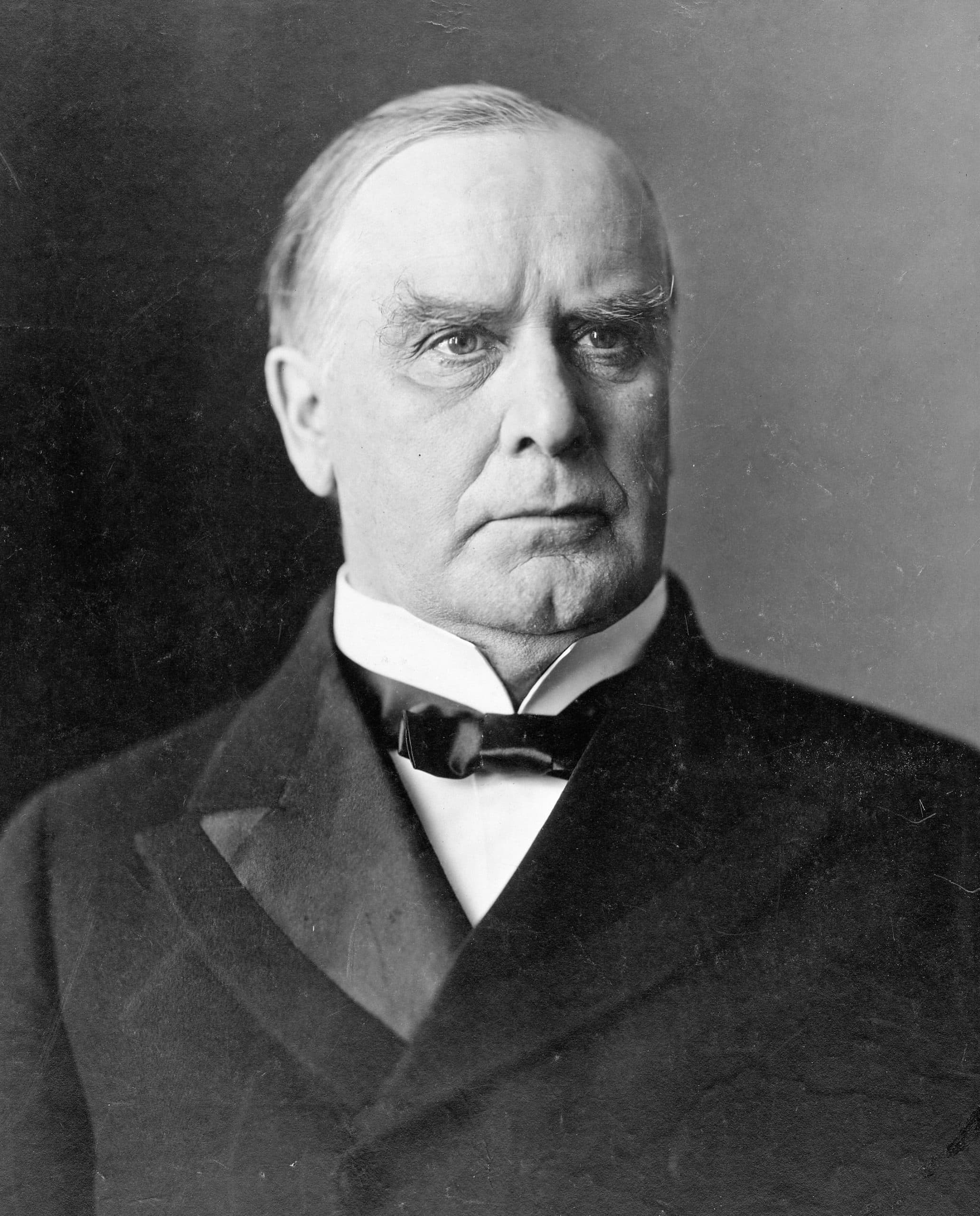 
| William McKinley | Republican | Stark | 1892 - 1896 |
| 40 |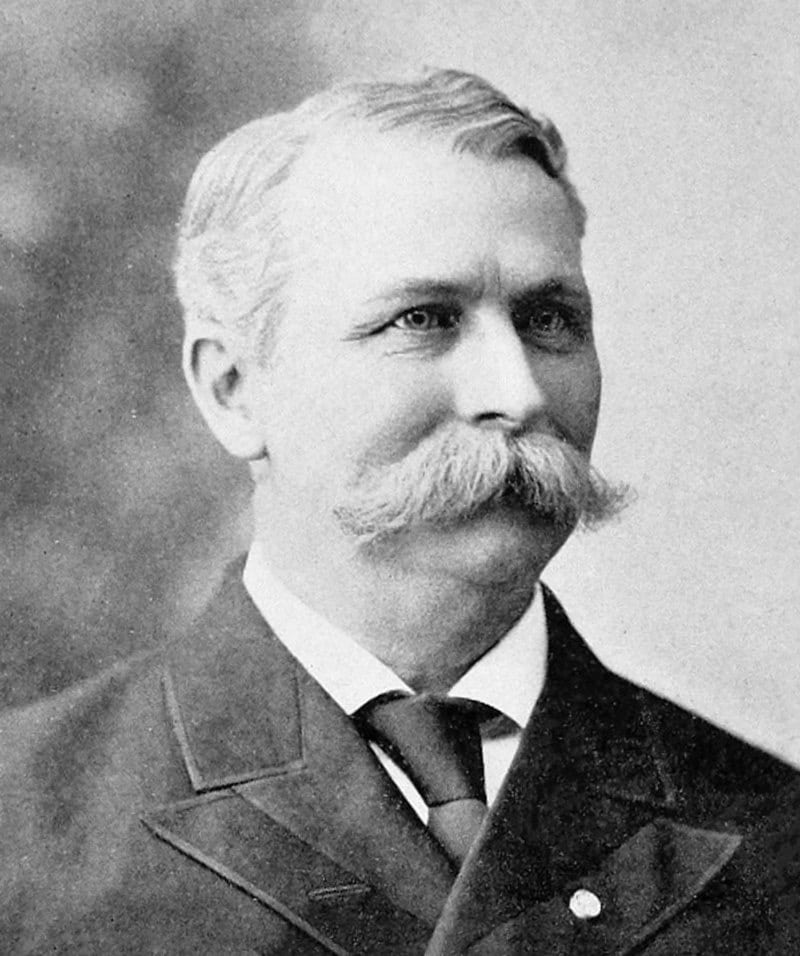 
| Asa Bushnell | Republican | Clark | 1896 -1900 |
| 41 | 
| George K. Nash | Republican | Medina | 1900 - 1904 |
| 42 | 
| Myron T. Herrick | Republican | Lorain | 1904 - 1906 |
| 43 | 
| John M. Pattison | Democrat | Clermont | 1906 |
| 44 | 
| Andrew L. Harris | Republican | Preble | 1906 - 1909 |
| 45 | 
| Judson Harmon | Democrat | Hamilton | 1909 - 1913 |
| 46 | 
| James M. Cox | Democrat | Montgomery | 1913 - 1915 |
| 47 | 
| Frank B. Willis | Republican | Delaware | 1915 - 1917 |
| 48 | 
| James M. Cox | Democrat | Montgomery | 1917 - 1921 |
| 49 |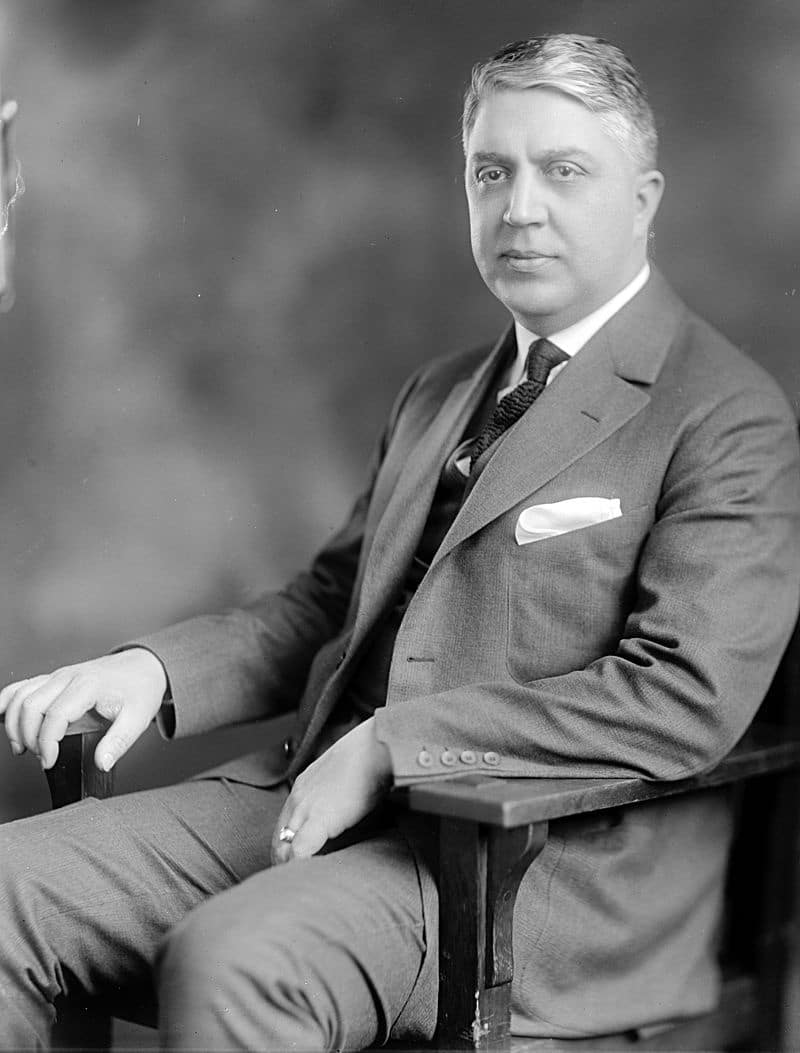 
| Harry L. Davis | Republican | Cuyahoga | 1921 - 1923 |
| 50 | 
| A. Victor Donahey | Democrat | Tuscarawas | 1923 - 1929 |
| 51 |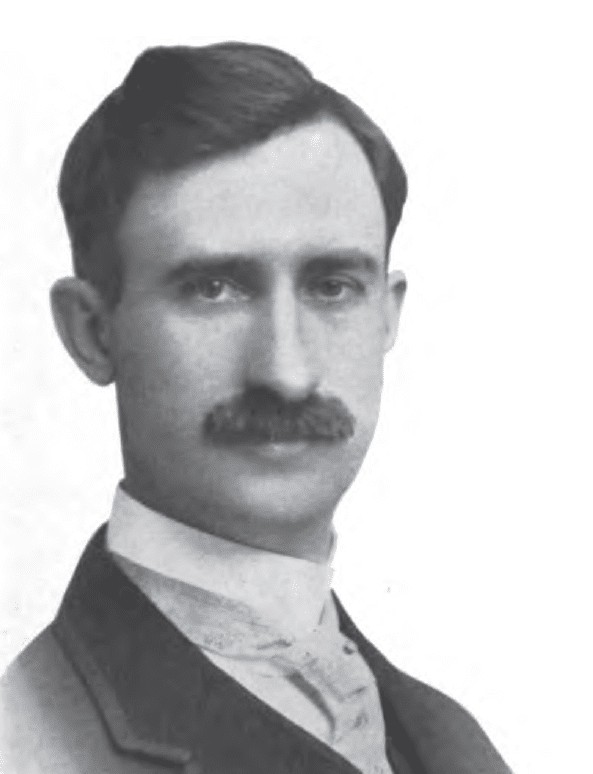  | Myers Y. Cooper | Republican | Hamilton | 1929 - 1931 |
| 52 |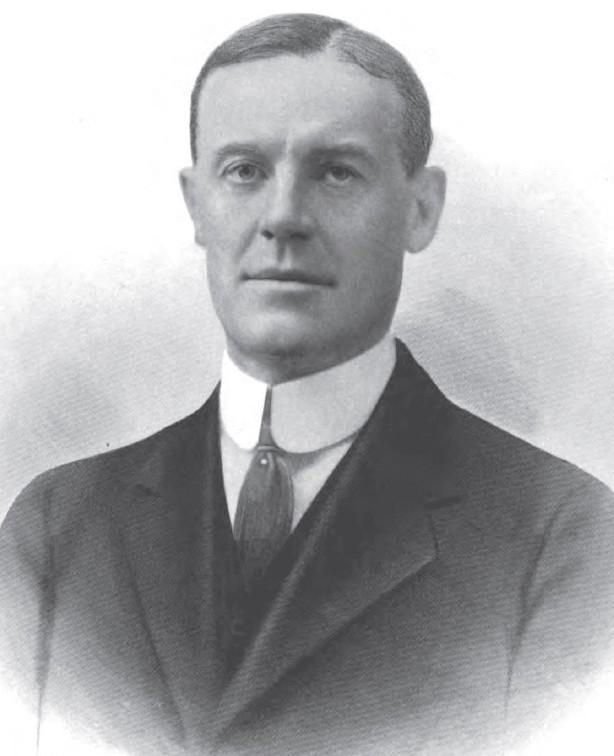  | George White | Democrat | Washington | 1931 - 1935 |
| 53 |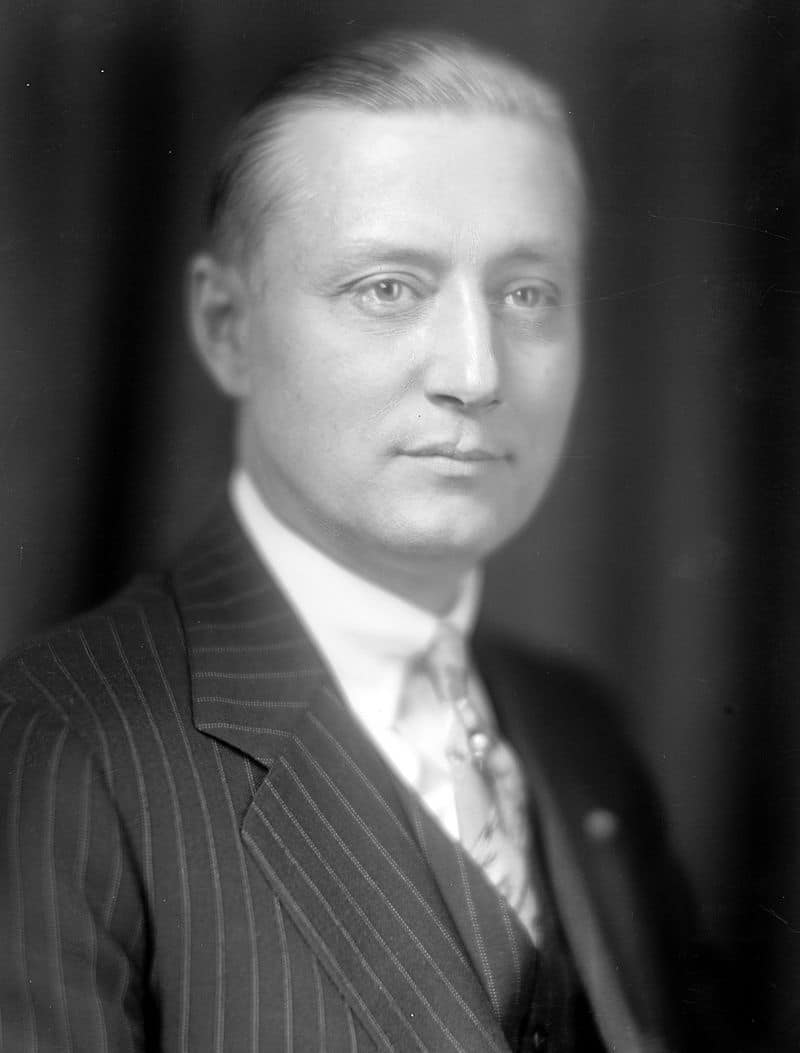 
| Martin L. Davey | Democrat | Portage | 1935 - 1939 |
| 54 |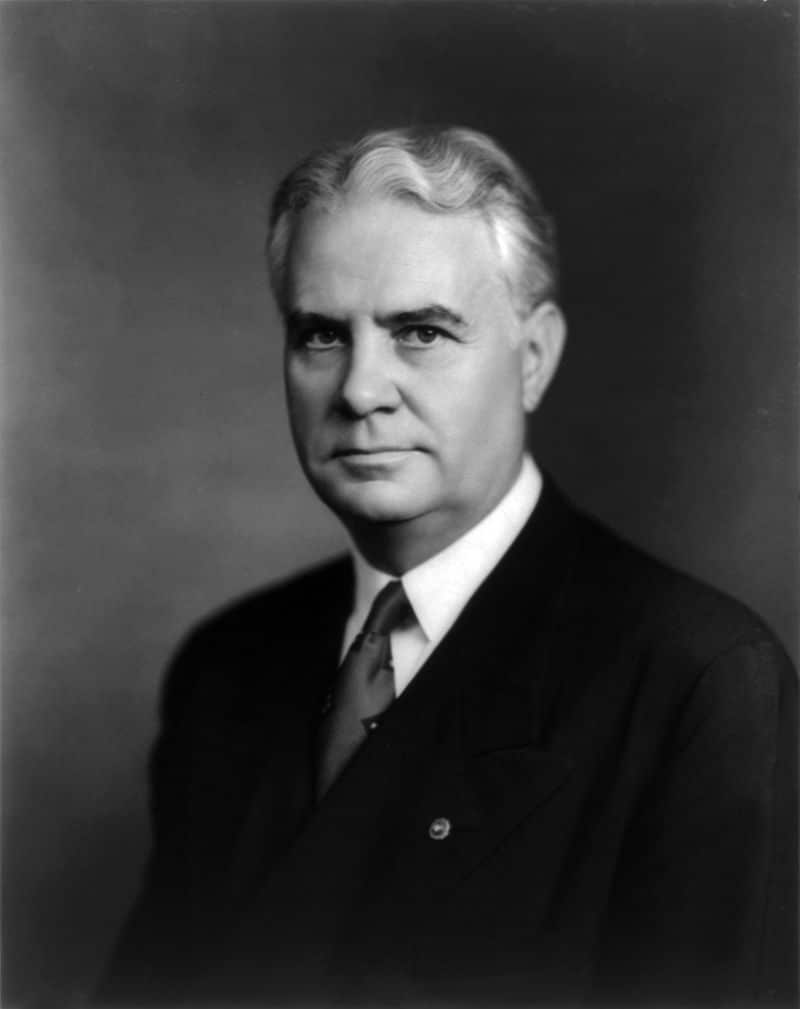 
| John W. Bricker | Republican | Franklin | 1939 - 1945 |
| 55 | 
| Frank Lausche | Democrat | Cuyahoga | 1945 - 1947 |
| 56 |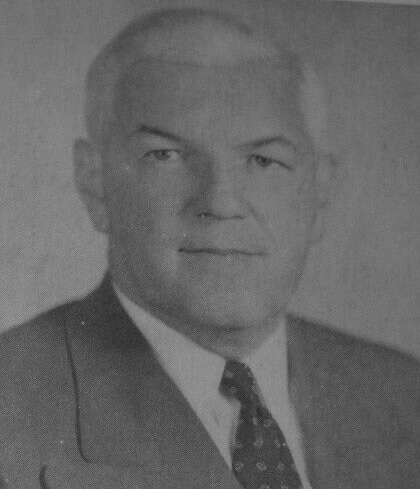 
| Thomas J. Herbert | Republican | Cuyahoga | 1947 - 1949 |
| 57 | 
| Frank Lausche | Democrat | Cuyahoga | 1949 - 1957 |
| 58 | 
| John W. Brown | Republican | Medina | 1957 |
| 59 | 
| C. William O'Neil | Republican | Washington | 1957 - 1959 |
| 60 |  | Michael Disalle | Democrat | Lucas | 1959 - 1963 |
| 61 |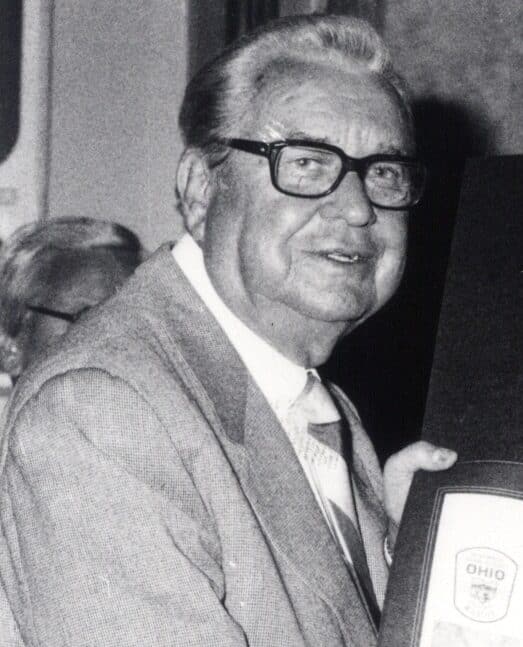 
| James Rhodes | Republican | Franklin | 1963 - 1971 |
| 62 |  | John Gilligan | Democrat | Hamilton | 1971 - 1975 |
| 63 | 
| Jim Rhodes | Republican | Franklin | 1975 - 1983 |
| 64 | 
| Richard Celeste | Democrat | Cuyahoga | 1983 - 1991 |
| 65 | 
| George Voinovich | Republican | Cuyahoga | 1991 - 1998 |
| 66 | 
| Nancy Hollister | Republican | Washington | 1998 - 1999 |
| 67 | 
| Bob Taft | Republican | Franklin | 1999 - 2007 |
| 68 | 
| Ted Strickland | Democrat | Scioto | 2007 - 2011 |
| 69 | 
| John Kasich | Republican | Delaware | 2011 - 2019 |
| 70 | 
| Mike DeWine | Republican | Greene | 2019 - Present |
FAQs of Ohio Governors
Wartime Governors
Who was the governor of Ohio during the War of 1812?
Return J Meigs
Who were the governors of Ohio during the Civil War?
William Dennison Jr., David Tod, and John Brough
Who were the governors of Ohio during World War 1?
James B. Cox (served non-consecutive terms) and Frank B. Willis
Who were the governors of Ohio during World War II?
John W. Bricker and Frank Lausche
General Questions
Where does the governor of Ohio live?
The Governor's Mansion is located in Bexley, Ohio. Bexley is a suburb of Columbus, Ohio.
What is the governor of Ohio's salary?
$148,886
Who was the first governor of Ohio?
Edward Tiffin
What Ohio Governor served in office the longest?
James Rhodes
How Many Ohio Governors Became President?
Two: Rutherford B. Hayes and William McKinley
How many have served as the governor of Ohio?
70
